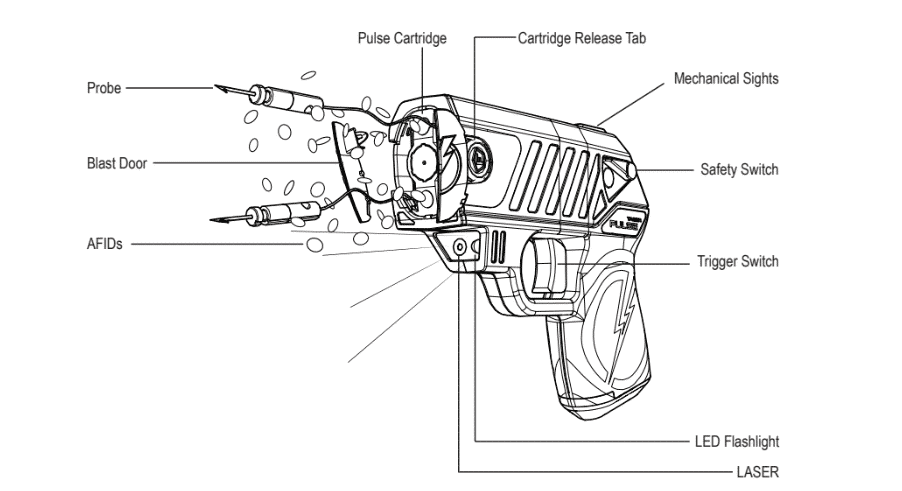
Unraveling the Tazer Mystery
Ever wondered what Tazers really are? Curious about their functionalities, their inner workings, and their significance in today’s society? You’re at the right place! This guide aims to unpack everything you need to know about Tazers.



Since its initial introduction, TASER – or as we often refer to it, Tazer – technology has undergone multiple transformations. The various versions or ‘generations’ of Tazers brought unique features and significant advancements over their predecessors. Let’s journey back to where it all started and trace the progression of this critical technology.
-
Design and Operation: The original TASER burst onto the law enforcement scene in 1974. This first-generation TASER fired a cartridge comprising two small probes tethered to the weapon through thin, high-voltage insulated wires. The device’s objective was to overload the sensory nervous system, effectively stunning the target.
-
Classification as a Firearm: Because these cartridges employed gunpowder as a propellant, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms (BATF) classified the 1974 TASER as a firearm.

- Non-Firearm Status: A pivotal moment in Tazer history, the second-generation Tazer – the AUR TASER 34000 series – introduced in 1994, brought several enhancements that led to its non-classification as a firearm by the BATF.

-
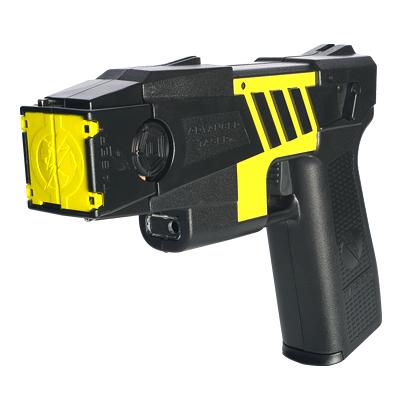
Design and Output Overhaul: The Advanced TASER M26, launched in 1999, ushered in a new era for Tazers. Apart from a complete makeover in its physical design that resembled a standard duty pistol, the M26 also differed in its output from previous versions.
-
Popularity Among Law Enforcement: The M26 quickly gained popularity as a safe, effective, and user-friendly non-lethal weapon among law enforcement agencies.

-
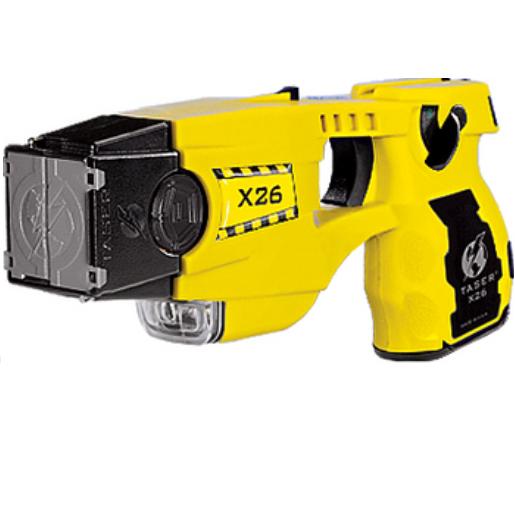
Size and Efficiency Improvements: In a quest for improved size, weight, and efficiency, the fourth-generation TASER, the X26, was introduced. This model, being smaller, lighter, and more effective than its predecessors, also incorporated numerous new features.
-
The Gold Standard: The TASER International X26 set the new benchmark for conducted energy weapons, enhancing officer and suspect safety by reducing potential injuries.

Through each iteration, Tazers have been refined, reshaped, and optimized to become the critical law enforcement tools they are today. Their historical evolution showcases continuous improvements in user safety, efficiency, and adaptability to the field’s changing needs.
Tazer vs. TASER: Dispelling the Confusion
Interestingly, although the term ‘Tazer‘ is widely used, the correct term is actually ‘TASER’, an acronym for ‘Thomas A. Swift’s Electric Rifle’. This fact is derived from the inspiration of the original inventor from a fictional character’s electric rifle. Over time, however, the name ‘Tazer’ gained more traction due to its easier pronunciation.
Understanding How Tazers Work
With a glimpse into their history and nomenclature, let’s now delve into the intriguing science that powers Tazers.
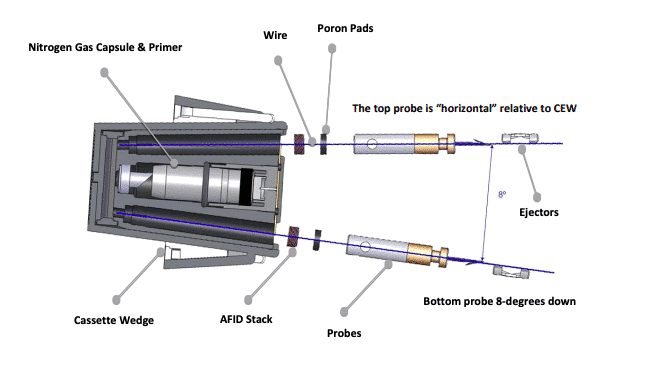
Tazer Technology: A Closer Look
Simply put, Tazers function by discharging an electric pulse that disrupts communication from nerves to muscles, leading to temporary incapacitation.
Safety First: A Core Principle in Tazer Design
For safety considerations, Tazers are designed with control features that limit the electric discharge, minimizing chances of causing permanent harm.
Varieties of Tazers: Know Your Options
Like most products, Tazers come in different shapes and sizes, each intended for a specific user or application.




Drawing the Line: Stun Guns vs. Tazer Guns
‘Stun gun’ and ‘Tazer gun’ are terms that are often used interchangeably. However, these two differ fundamentally in their mechanisms, operational distances, and effects on the target. Here’s a detailed comparison to help you understand the differences:
Stun Guns
-
Direct Contact Required: Stun guns require direct contact with the target to deliver their electric charge. This necessitates close proximity to the assailant, which could potentially put the user at risk.
-
Electrical Discharge Mechanism: Stun guns work by delivering a high-voltage, low-amperage shock to the target. This shock is enough to cause considerable pain and involuntary muscle contractions, but not enough to cause severe injury or incapacitation.
-
Lack of Neuro-Muscular Incapacitation: The electrical shock from a stun gun primarily causes pain compliance, not neuromuscular incapacitation. Therefore, if the target is sufficiently determined, intoxicated, or under the influence of certain drugs, they might be able to withstand the shock.
-
Limited After-Effect: Once the shock ceases, the target can usually regain their faculties quite quickly, posing a potential risk to the user.
Tazer Guns
-
Operational Distance: Unlike stun guns, Tazers can be used from a distance, typically up to 15 feet. This provides a significant safety advantage by allowing the user to incapacitate a threat without having to be within arm’s reach.
-
Electrical Discharge Mechanism: Tazers function by shooting two dart-like electrodes, which are connected to the Tazer by conductive wires, towards the target. Upon contact, the Tazer delivers a pulse that disrupts the body’s neuromuscular system, leading to temporary incapacitation.
-
Neuro-Muscular Incapacitation: The electrical discharge from a Tazer causes a disruption in the communication between the brain and muscles, leading to a loss of control and temporary incapacitation. This effect is independent of pain tolerance or the influence of substances, making Tazers more reliable in various scenarios.
-
Prolonged After-Effect: The effects of a Tazer can last for several minutes, providing the user enough time to escape or get help.
By understanding these differences, you can better decide which self-defense tool suits your needs best.
Choosing Your Tazer: A Guide to Making the Right Choice
Choosing a Tazer involves considerations ranging from size and design to power and additional safety features. It’s crucial to consider your personal needs, legal limitations, and safety in the selection process.
The Safe Use of Tazers: A Must-Know
While Tazers can be an effective tool, mastering their safe usage is crucial for any user.
The Importance of Tazer Training
Proper training can significantly enhance the safe and effective use of a Tazer. This includes understanding when and how to deploy the Tazer and what actions to take afterward.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Tazers
With a clear understanding of their workings and the different types, let’s assess the effectiveness of Tazers in real-life situations.
Tazers in Action
Tazers have proven their worth in numerous real-world scenarios, offering a non-lethal alternative for self-defense and law enforcement.

The Legal and Ethical Implications of Tazer Use
The use of Tazers is not without legal and ethical implications. It’s essential to fully understand these aspects before purchasing or using a Tazer. Understand your Tazer Gun Laws before you purchase.

Final Thoughts: Knowledge is Power
In conclusion, Tazers are indeed game-changers in the realm of non-lethal defense and law enforcement. However, their use should always be accompanied by a comprehensive understanding and proper training.

Frequently Asked Questions
-
What exactly is a Tazer? A Tazer is a non-lethal device used to temporarily incapacitate individuals through a high-voltage electric pulse.
-
How do Tazers function? Tazers disrupt the neuromuscular system with an electric charge, causing short-term incapacitation.
-
How do stun guns and Tazers differ? The main distinction lies in the delivery of the electric charge. A stun gun requires direct contact, while a Tazer can be used from a distance.
-
Can civilians legally own Tazers? The legality of Tazer ownership by civilians varies across countries and regions. Therefore, always check your local regulations before purchasing or carrying a Tazer.
-
Are Tazers dangerous? Although Tazers are designed as non-lethal devices, they can cause injury if used incorrectly. Therefore, safety training and correct handling are of utmost importance.